 The rise of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly natural language processing models like ChatGPT and Gemini, is gradually transforming medical practice, including in nephrology. This article explores the current and future applications of AI in this field, highlighting the opportunities, limitations, and ethical issues.
Clinical Applications of AI in Nephrology
AI, particularly through machine learning, is already used to:
• Predict acute kidney injury;
• Analyze medical images (e.g., renal volumetry in polycystic kidney disease);
• Assess the risk of progression to end-stage renal disease, particularly in IgA nephropathy;
• Optimize anemia management and prevent hypotension in dialysis;
• Predict kidney graft survival using internationally validated models such as iBox.
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly natural language processing models like ChatGPT and Gemini, is gradually transforming medical practice, including in nephrology. This article explores the current and future applications of AI in this field, highlighting the opportunities, limitations, and ethical issues.
Clinical Applications of AI in Nephrology
AI, particularly through machine learning, is already used to:
• Predict acute kidney injury;
• Analyze medical images (e.g., renal volumetry in polycystic kidney disease);
• Assess the risk of progression to end-stage renal disease, particularly in IgA nephropathy;
• Optimize anemia management and prevent hypotension in dialysis;
• Predict kidney graft survival using internationally validated models such as iBox.
Towards Precision Nephrology
The integration of "omics" data (genomics, proteomics, transcriptomics) paves the way for personalized medicine. However, their use by AI still requires technological advances and close interdisciplinary collaboration.
Generative AI in Clinical Practice
Tests conducted with chatbots (ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, Mistral AI) on clinical cases show promising, though sometimes inaccurate, results. Perplexity stood out for the quality of its up-to-date responses, while ChatGPT provided complete answers but with some citation errors.
Ethical and Regulatory Issues
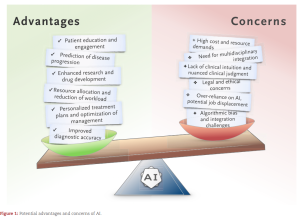
The use of AI in healthcare raises major concerns :
• Data protection and patient safety;
• Algorithm transparency (black box syndrome);
• Risk of overreliance on junior clinicians;
• Equitable access to technologies, particularly in low- and middle-income countries.
The European Union recently adopted the "Artificial Intelligence Act," classifying AI systems in healthcare as "high-risk," imposing strict requirements for data quality, human oversight, and risk assessment.
Conclusion :
AI represents an essential and potentially revolutionary advancement for nephrology. However, its integration must be guided by ethical considerations, appropriate training for healthcare professionals, and interdisciplinary collaboration. The goal is to combine the capabilities of AI with human clinical judgment to improve patient care.
 The rise of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly natural language processing models like ChatGPT and Gemini, is gradually transforming medical practice, including in nephrology. This article explores the current and future applications of AI in this field, highlighting the opportunities, limitations, and ethical issues.
Clinical Applications of AI in Nephrology
AI, particularly through machine learning, is already used to:
• Predict acute kidney injury;
• Analyze medical images (e.g., renal volumetry in polycystic kidney disease);
• Assess the risk of progression to end-stage renal disease, particularly in IgA nephropathy;
• Optimize anemia management and prevent hypotension in dialysis;
• Predict kidney graft survival using internationally validated models such as iBox.
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI), particularly natural language processing models like ChatGPT and Gemini, is gradually transforming medical practice, including in nephrology. This article explores the current and future applications of AI in this field, highlighting the opportunities, limitations, and ethical issues.
Clinical Applications of AI in Nephrology
AI, particularly through machine learning, is already used to:
• Predict acute kidney injury;
• Analyze medical images (e.g., renal volumetry in polycystic kidney disease);
• Assess the risk of progression to end-stage renal disease, particularly in IgA nephropathy;
• Optimize anemia management and prevent hypotension in dialysis;
• Predict kidney graft survival using internationally validated models such as iBox.